Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves the fusion of male and female gametes, leading to the formation of a genetically unique offspring. Unlike asexual reproduction, which produces clones, sexual reproduction results in genetic variation due to the combination of genes from two parents.
Key Features of Sexual Reproduction:
- Involvement of Two Parents: Typically, a male and a female contribute gametes.
- Gamete Formation: Specialized reproductive cells (sperm in males, eggs in females) are formed through meiosis, ensuring genetic diversity.
- Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gametes forms a zygote, which develops into a new organism.
- Genetic Variation: Offspring inherit a mix of genetic traits from both parents, leading to diversity within a population.
Phases of Sexual Reproduction:
- Pre-fertilization Events:
- Gametogenesis: Formation of male and female gametes.
- Gamet Transfer: Movement of gametes to the site of fertilization.
- Fertilization:
- Fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- Post-fertilization Events:
- Zygote Formation: The zygote develops into an embryo and eventually grows into a new individual.
Example: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
In flowering plants:
- Male gamete (pollen) is produced in the anther.
- Female gamete (egg) is found in the ovule within the ovary.
- Pollination: Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
- Fertilization: The pollen tube grows towards the ovule, and the male gamete fuses with the female gamete, forming a zygote, which develops into a seed.
Let me draw an image showing the process of sexual reproduction using a flowering plant and the stages of gamete fusion and zygote formation.
See in Fig.
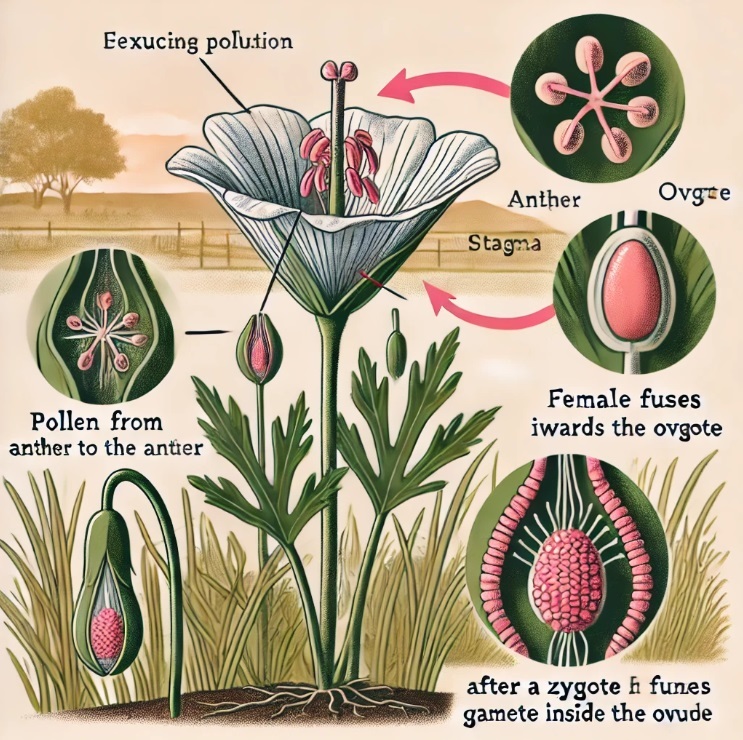
Here is the illustration of sexual reproduction in a flowering plant, showing the key stages such as pollination, pollen tube formation, and the fusion of male and female gametes leading to the formation of a zygote. The image highlights how sexual reproduction in plants leads to genetic variation and the development of seeds.