Reproductive Health and Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Reproductive health is an essential aspect of overall well-being, and it refers to the ability of individuals to have a safe and satisfying sex life, with the freedom to decide if, when, and how often to reproduce. It also encompasses the right to access safe, effective, and affordable family planning services and health care for maternal and infant care. Maintaining reproductive health is crucial for ensuring the well-being of individuals and communities. One important aspect of reproductive health is the prevention and management of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs).
What are Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs), also known as Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), are infections that are primarily spread through sexual contact. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites and can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Some STDs can also be spread through non-sexual means, such as from mother to baby during childbirth or through sharing needles.
Common STDs and Their Causes
- Chlamydia: A bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, which can affect both men and women. It often shows no symptoms, but it can cause serious complications like infertility if left untreated.
- Gonorrhea: Caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, it can infect the genital tract, mouth, and rectum. Symptoms include burning sensations during urination and abnormal discharge from the genitals.
- Syphilis: This bacterial infection caused by Treponema pallidum progresses in stages, each with different symptoms. It can lead to severe health issues such as heart problems and neurological disorders if not treated.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): A viral infection that can lead to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). HIV weakens the immune system, making the body vulnerable to infections and certain cancers.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV-1 and HSV-2 cause oral and genital herpes, respectively. Symptoms include painful sores or blisters around the mouth or genital area.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): A viral infection that affects the skin and mucous membranes. Certain types of HPV can lead to genital warts and are associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer.
- Trichomoniasis: A parasitic infection caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, resulting in itching, burning, and discharge.
- Hepatitis B: A viral infection that affects the liver, which can be transmitted sexually or through contact with infected blood.
Symptoms of STDs
STDs can present a range of symptoms, while some may show no symptoms at all. Common symptoms may include:
- Unusual genital discharge
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Sores, bumps, or rashes around the genitals, anus, or mouth
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Itching or irritation in the genital area
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the groin area
Some STDs like HIV may not show symptoms for a long time but still cause significant damage to the immune system.
Complications of Untreated STDs
If left untreated, STDs can lead to serious health complications, such as:
- Infertility: Chlamydia and gonorrhea can damage the reproductive organs, leading to infertility in both men and women.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): In women, untreated bacterial STDs can lead to PID, a painful condition that affects the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
- Increased Risk of HIV: Having an STD can increase the risk of acquiring HIV because the infections can cause sores or breaks in the skin, making it easier for HIV to enter the body.
- Pregnancy Complications: STDs can be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, leading to complications such as low birth weight, premature delivery, and neonatal infections.
- Cancer: HPV infection can lead to cervical, penile, and oropharyngeal cancers.
Prevention of STDs
Preventing STDs is crucial for maintaining reproductive health. The following strategies can reduce the risk:
- Condom Use: Using condoms correctly and consistently during sexual activity can significantly reduce the risk of STDs.
- Vaccination: Vaccines are available for certain STDs, such as HPV and hepatitis B, which can help prevent these infections.
- Regular Screening: Regular testing for STDs is important, especially for sexually active individuals or those with multiple partners. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and reduces the risk of complications.
- Limiting Sexual Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners and engaging in mutually monogamous relationships with partners who have been tested for STDs can lower the risk.
- Avoiding Substance Abuse: Alcohol and drug use can impair judgment and lead to risky sexual behavior, increasing the risk of STDs.
- Education and Awareness: Public health education about safe sex practices, proper condom use, and the importance of getting tested for STDs can help prevent their spread.
Treatment of STDs
The treatment for STDs depends on the type of infection:
- Bacterial STDs (e.g., chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis): These can usually be treated effectively with antibiotics. It’s important to complete the full course of treatment even if symptoms improve.
- Viral STDs (e.g., herpes, HIV, hepatitis B): While there is no cure for these infections, antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of transmission.
- Parasitic STDs (e.g., trichomoniasis): These can be treated with antiparasitic medications.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and reduce the spread of STDs.
Reproductive Health Services
Access to reproductive health services is essential for managing STDs and maintaining overall reproductive health. Services include:
- STD Testing and Treatment: Clinics and healthcare providers offer testing for STDs and provide necessary treatment.
- Counseling and Education: Health professionals offer advice on safe sex practices, contraception, and STD prevention.
- Contraceptive Services: Access to birth control options helps prevent unintended pregnancies and reduces the risk of certain STDs.
- Prenatal and Maternal Care: Regular health checkups during pregnancy help prevent complications related to STDs.
The Role of Education in Reproductive Health
Education plays a significant role in promoting reproductive health and preventing STDs. Comprehensive sex education programs provide information about:
- Safe sex practices, including the use of condoms and contraceptives
- The importance of regular STD testing and early treatment
- Understanding consent and making informed decisions about sexual activity
- The biological and psychological aspects of sexual health
Educating young people about these topics can help them make responsible choices and prevent the spread of STDs.
Example Scenario: Understanding the Impact of an Untreated STD
Consider a 22-year-old woman named Anika who experiences irregular menstrual cycles and pelvic pain. She dismisses these symptoms as typical period-related issues. Over time, the pain intensifies, and she notices unusual vaginal discharge. Anika eventually visits a healthcare provider who diagnoses her with pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a complication arising from untreated chlamydia.
Anika learns that she had contracted chlamydia from a partner and had not undergone any STD screening. The untreated infection spread to her reproductive organs, causing inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes. As a result, her risk of infertility increased significantly, and she might need surgical intervention in the future.
This scenario illustrates the importance of regular STD screening and early treatment. Anika could have avoided complications if she had sought timely medical care.
Reproductive Health Challenges
Maintaining reproductive health comes with various challenges, such as:
- Stigma and Discrimination: Many people avoid getting tested for STDs due to the stigma attached to them, leading to undiagnosed and untreated infections.
- Lack of Access to Health Services: In some regions, reproductive health services may not be readily available or affordable, limiting access to STD testing and treatment.
- Cultural Barriers: Some cultural and religious beliefs discourage open discussions about sexual health, which can hinder education and preventive measures.
- Misinformation: Misleading or incorrect information about STDs and reproductive health can prevent individuals from taking appropriate actions to protect themselves.
Promoting Reproductive Health
To address these challenges, several actions can be taken:
- Improving Access to Healthcare: Ensuring affordable and accessible reproductive health services for all.
- Comprehensive Sex Education: Providing accurate information on safe sex practices, contraception, and the importance of regular STD screening.
- Combating Stigma: Raising awareness and normalizing conversations about STDs to reduce stigma and encourage testing and treatment.
- Government and NGO Initiatives: Supporting public health campaigns and initiatives that promote reproductive health and provide resources to underserved communities.
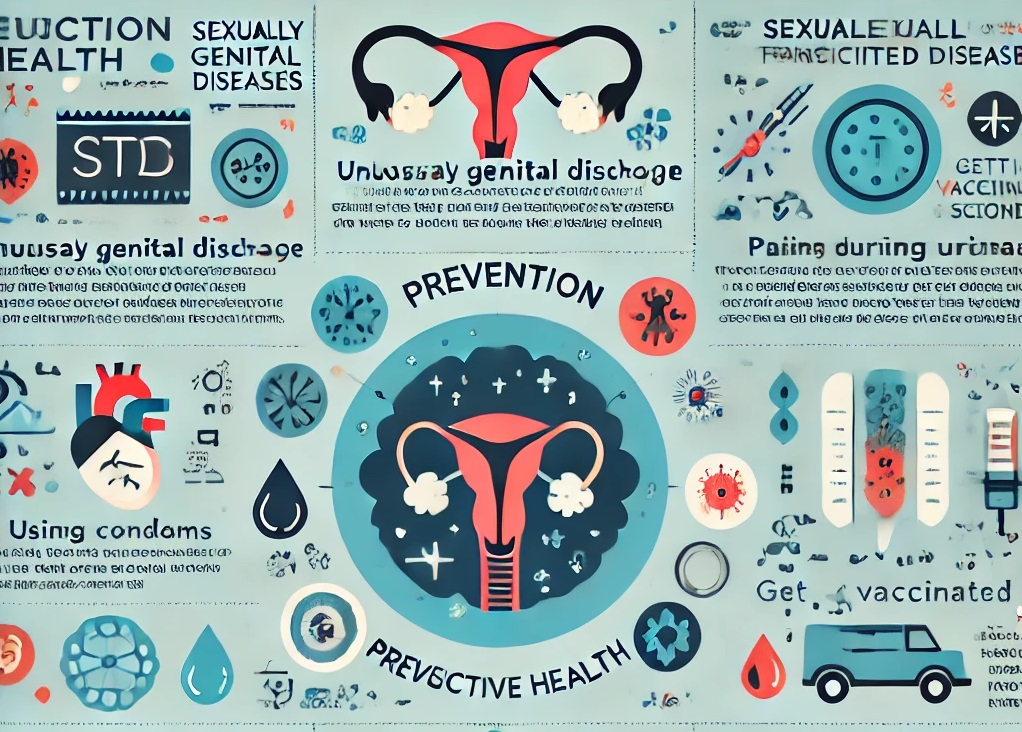
See in Fig:

The infographic above highlights essential information on reproductive health, including the symptoms and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). It provides an overview of common symptoms such as unusual genital discharge, pain during urination, and sores, along with prevention tips like using condoms, getting vaccinated, and regular screening.